RFID Blood Banks
- Home
- Pages
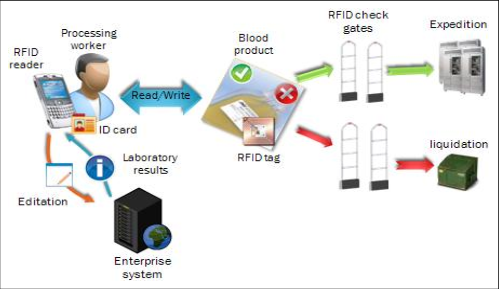
RFID Solution Of Blood Bank
The RFID solution is to embed a tag into the blood bag label itself. The paramedic who transfuses the blood can scan the bag before transferring. He/she typically enters the patient ID number, or in a better system, the patient also has a wristband RFID tag which identifies him uniquely.
In case the wrong blood bag is scanned, the reader can throw up a warning like this :
The blood bag is for the Patient:
- JOHN SMITH.
Patient ID 3S1002453 - The patient on the bed is:
- JOHN SMITH.
Patient ID 3S1002453.
Patient ID JS1003453.
This will save the life of Mr. John Smith (who will no doubt, be eternally grateful to the technology, if only he knew what was about to happen!)
Present Situation Of Blood Bank
In thousands of hospitals across the world, blood transfusion is an everyday business, but fraught with risks. This is, not only because contaminated blood may be transfused into an otherwise healthy patient, but also because he may receive the wrong type of blood altogether.
Why have the number of mistakes occurred and worstly increased? This is because many hospitals have cut back staff due to cost pressures. The person who collects blood is not the same person who transfuses it. Typically the patient is not known personally to the nurse who administers the transfusion. The misidentification can occur due to overwork, carelessness, or any other factors. What is important is that it does take place. After the event, there is no point in blaming people, processes, or institutions because preventing such incidents is to be the main thought. And, due to RFID technology, these errors are completely preventable. In a typical hospital emergency room, the following situation is not unimaginable :
- There has been an accident and a large number of victims have been brought in.
- Suddenly a large amount of blood is needed for the emergency procedures to be carried out on these patients.
- The patient himself is either asleep, sedated, or otherwise unconscious, unable to talk or communicate with the paramedics.
- The nurse or paramedic does not know the patient personally
One sees that the nurse or paramedic can easily pick up the wrong blood bag, get confused because of similar sounding names, and hence transfuse the wrong blood. This is in most cases, fatal.
Advantages Of Using RFID
- No errors at all, even in case of demanding and panic-like situations. This itself can be said to be the ROl of an investment in such a system. Saving a few lives a year is worth the cost of a few tags & readers!
- Can be used for other body fluids or patient dosages too, and need not be restricted to only blood. For example medicine dosages, intravenous drips, etc.
- Offers traceability and tracking, can evaluate the actual level of patient care that is offered by the nurses, to upper management, using data collection. For example, middleware can be used to match queries like “How much time did nurse Jensen spend between collecting the blood from the blood bank and transfusing it into Mr. Smith” and so on, which is invaluable to provide better quality of service to patients.
- RFID Fixed Asset Management
- RFID Anti-Theft Systems
- RFID Jewellery Tracking System
- RFID Untouched Attendance
- RFID Warehouse Management
- RFID Animal Identification
- RFID Vehicle Identification
- RFID ETC(Electronic Toll Collection) Solution
- RFID Laundry Management
- RFID Student/Parent Auto Voice Calling at School
- RFID Royalty Customers Deals at Shopping Malls
- RFID Document Management
- RFID Anesthetic Dosages
- RFID Baggage Handling
- RFID Blood Banks
- RFID People & Personnel Tracking
- RFID Car manufacturing
- RFID Drug Pedigree
- RFID Event Management
- RFID Race Solution Sports Events
- RFID Food Safety
- RFID National Identification
- RFID Gasoline Dispensing
- RFID Hotels & Resorts
- RFID Work in Progress Tracking
- RFID Hospital Stores Management
- RFID Medical Surgeries
- RFID Based Patient Location Confirmation
- RFID Body Temperature Monitoring System
- RFID Body Temperature Monitoring for Employees
- RFID Mother Baby Pairing
- RFID Museums
- RFID Spool Tracking System
- RFID Plane Spare Parts
- RFID Industry 4.0 Smart Manufacturing
- RFID Container Tracking System
- RFID Intelligent RFID Parking System
- RFID Office Printers & Cartridges
- RFID Real Time Location Tracking (RTLS)
- RFID Retailing
- RFID Underground Sewers
- RFID Forklift Automation
- RFID Sales Staff Tracking at Shopping Malls
- RFID Trial Room Analytics at Shopping Malls
- RFID Traffic Management
- RFID Guard Patrolling System
- RFID Weightbridge Automation System
- RFID E-Lock for Contrainers
- RFID E-Seal for Contrainers
- RFID Waste Management
- RFID Yard Management

Can we help you?

